Middleware
You can run code before and after your Slim application to manipulate the Request and Response objects as you see fit. This is called middleware. Why would you want to do this? Perhaps you want to protect your app from cross-site request forgery. Maybe you want to authenticate requests before your app runs. Middleware is perfect for these scenarios.
What is middleware?
A middleware implements the PSR-15 Middleware Interface:
Psr\Http\Message\ServerRequestInterface- The PSR-7 request objectPsr\Http\Server\RequestHandlerInterface- The PSR-15 request handler object
It can do whatever is appropriate with these objects.
The only hard requirement is that a middleware MUST return an instance of Psr\Http\Message\ResponseInterface.
Each middleware SHOULD invoke the next middleware and pass it the Request object as argument.
How does middleware work?
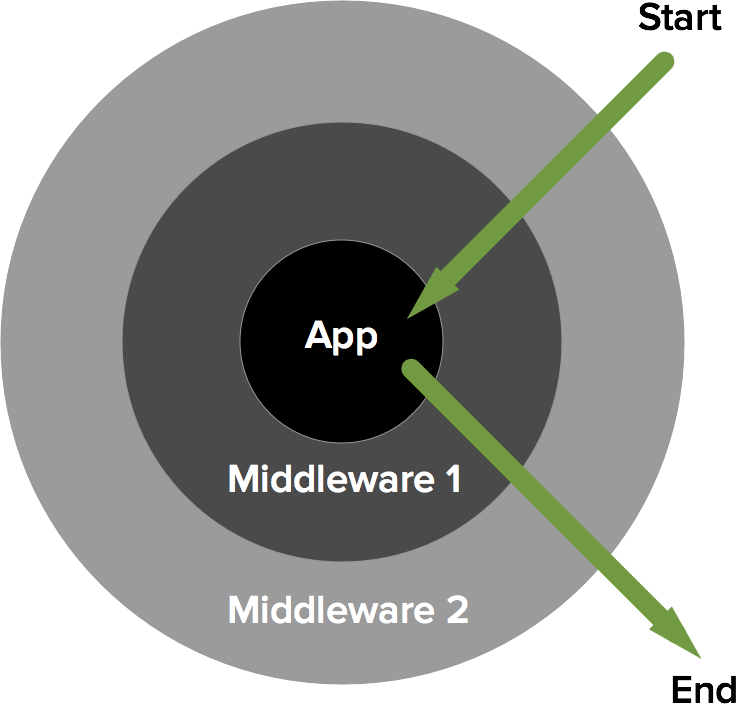
Different frameworks use middleware differently. Slim adds middleware as concentric layers surrounding your core application. Each new middleware layer surrounds any existing middleware layers. The concentric structure expands outwardly as additional middleware layers are added.
The last middleware layer added is the first to be executed.
When you run the Slim application, the Request object traverses the middleware structure from the outside in. They first enter the outermost middleware, then the next outermost middleware, (and so on), until they ultimately arrive at the Slim application itself. After the Slim application dispatches the appropriate route, the resultant Response object exits the Slim application and traverses the middleware structure from the inside out. Ultimately, a final Response object exits the outermost middleware, is serialized into a raw HTTP response, and is returned to the HTTP client. Here’s a diagram that illustrates the middleware process flow:
How do I write middleware?
Middleware is a callable that accepts two arguments: a Request object and a RequestHandler object.
Each middleware MUST return an instance of Psr\Http\Message\ResponseInterface.
Closure middleware example.
This example middleware is a Closure.
<?php
use Psr\Http\Message\ResponseInterface;
use Psr\Http\Message\ServerRequestInterface as Request;
use Psr\Http\Server\RequestHandlerInterface as RequestHandler;
use Slim\Factory\AppFactory;
require __DIR__ . '/../vendor/autoload.php';
$app = AppFactory::create();
/**
* Example middleware closure
*
* @param Request $request PSR-7 request
* @param RequestHandler $handler PSR-15 request handler
*
* @return ResponseInterface
*/
$beforeMiddleware = function (Request $request, RequestHandler $handler) use ($app) {
$response = $handler->handle($request);
$existingContent = (string) $response->getBody();
$response = $app->getResponseFactory()->createResponse();
$response->getBody()->write('BEFORE' . $existingContent);
return $response;
};
$afterMiddleware = function ($request, $handler) {
$response = $handler->handle($request);
$response->getBody()->write('AFTER');
return $response;
};
$app->add($beforeMiddleware);
$app->add($afterMiddleware);
// ...
$app->run();
Invokable class middleware example
This example middleware is an invokable class that implements the magic __invoke() method.
<?php
use Psr\Http\Message\ServerRequestInterface as Request;
use Psr\Http\Server\RequestHandlerInterface as RequestHandler;
use Psr\Http\Message\ResponseInterface as Response;
class ExampleBeforeMiddleware
{
/**
* Example middleware invokable class
*
* @param Request $request PSR-7 request
* @param RequestHandler $handler PSR-15 request handler
*
* @return Response
*/
public function __invoke(Request $request, RequestHandler $handler): Response
{
$response = $handler->handle($request);
$existingContent = (string) $response->getBody();
$response = new Response();
$response->getBody()->write('BEFORE' . $existingContent);
return $response;
}
}
<?php
use Psr\Http\Message\ResponseInterface as Response;
use Psr\Http\Message\ServerRequestInterface as Request;
use Psr\Http\Server\RequestHandlerInterface as RequestHandler;
class ExampleAfterMiddleware
{
/**
* Example middleware invokable class
*
* @param Request $request PSR-7 request
* @param RequestHandler $handler PSR-15 request handler
*
* @return Response
*/
public function __invoke(Request $request, RequestHandler $handler): Response
{
$response = $handler->handle($request);
$response->getBody()->write('AFTER');
return $response;
}
}
To use these classes as a middleware, you can use add(new ExampleMiddleware()); function chain after the $app route mapping methods get(), post(), put(), patch(), delete(), options(), any() or group(), as demonstrated in the code below.
<?php
use Slim\Factory\AppFactory;
require __DIR__ . '/../vendor/autoload.php';
$app = AppFactory::create();
// Add Middleware On App
$app->add(new ExampleMiddleware());
// Add Middleware On Route
$app->get('/', function () { ... })->add(new ExampleMiddleware());
// Add Middleware On Group
$app->group('/', function () { ... })->add(new ExampleMiddleware());
// ...
$app->run();
How do I add middleware?
You may add middleware to a Slim application, to an individual Slim application route or to a route group. All scenarios accept the same middleware and implement the same middleware interface.
Application middleware
Application middleware is invoked for every incoming HTTP request. Add application middleware with the Slim application instance’s add() method. This example adds the Closure middleware example above:
<?php
use Psr\Http\Message\ResponseInterface as Response;
use Psr\Http\Message\ServerRequestInterface as Request;
use Psr\Http\Server\RequestHandlerInterface as RequestHandler;
use Slim\Factory\AppFactory;
require __DIR__ . '/../vendor/autoload.php';
$app = AppFactory::create();
$app->add(function (Request $request, RequestHandler $handler) use ($app) {
$response = $handler->handle($request);
$existingContent = (string) $response->getBody();
$response = $app->getResponseFactory()->createResponse();
$response->getBody()->write('BEFORE ' . $existingContent);
return $response;
});
$app->add(function (Request $request, RequestHandler $handler) {
$response = $handler->handle($request);
$response->getBody()->write(' AFTER');
return $response;
});
$app->get('/', function (Request $request, Response $response, $args) {
$response->getBody()->write('Hello World');
return $response;
});
$app->run();
This would output this HTTP response body:
BEFORE Hello World AFTER
Route middleware
Route middleware is invoked only if its route matches the current HTTP request method and URI. Route middleware is specified immediately after you invoke any of the Slim application’s routing methods (e.g., get() or post()). Each routing method returns an instance of \Slim\Route, and this class provides the same middleware interface as the Slim application instance. Add middleware to a Route with the Route instance’s add() method. This example adds the Closure middleware example above:
<?php
use Psr\Http\Message\ResponseInterface as Response;
use Psr\Http\Message\ServerRequestInterface as Request;
use Psr\Http\Server\RequestHandlerInterface as RequestHandler;
use Slim\Factory\AppFactory;
require __DIR__ . '/../vendor/autoload.php';
$app = AppFactory::create();
$mw = function (Request $request, RequestHandler $handler) {
$response = $handler->handle($request);
$response->getBody()->write('World');
return $response;
};
$app->get('/', function (Request $request, Response $response, $args) {
$response->getBody()->write('Hello ');
return $response;
})->add($mw);
$app->run();
This would output this HTTP response body:
Hello World
Group middleware
In addition to the overall application, and standard routes being able to accept middleware, the group() multi-route definition functionality, also allows individual routes internally. Route group middleware is invoked only if its route matches one of the defined HTTP request methods and URIs from the group. To add middleware within the callback, and entire-group middleware to be set by chaining add() after the group() method.
Sample Application, making use of callback middleware on a group of url-handlers.
<?php
use Psr\Http\Message\ResponseInterface as Response;
use Psr\Http\Message\ServerRequestInterface as Request;
use Psr\Http\Server\RequestHandlerInterface as RequestHandler;
use Slim\Factory\AppFactory;
use Slim\Routing\RouteCollectorProxy;
require __DIR__ . '/../vendor/autoload.php';
$app = AppFactory::create();
$app->get('/', function (Request $request, Response $response) {
$response->getBody()->write('Hello World');
return $response;
});
$app->group('/utils', function (RouteCollectorProxy $group) {
$group->get('/date', function (Request $request, Response $response) {
$response->getBody()->write(date('Y-m-d H:i:s'));
return $response;
});
$group->get('/time', function (Request $request, Response $response) {
$response->getBody()->write((string)time());
return $response;
});
})->add(function (Request $request, RequestHandler $handler) use ($app) {
$response = $handler->handle($request);
$dateOrTime = (string) $response->getBody();
$response = $app->getResponseFactory()->createResponse();
$response->getBody()->write('It is now ' . $dateOrTime . '. Enjoy!');
return $response;
});
$app->run();
When calling the /utils/date method, this would output a string similar to the below.
It is now 2015-07-06 03:11:01. Enjoy!
Visiting /utils/time would output a string similar to the below.
It is now 1436148762. Enjoy!
But visiting / (domain-root), would be expected to generate the following output as no middleware has been assigned.
Hello World
Passing variables from middleware
The easiest way to pass attributes from middleware is to use the request’s attributes.
Setting the variable in the middleware:
$request = $request->withAttribute('foo', 'bar');
Getting the variable in the route callback:
$foo = $request->getAttribute('foo');
Finding available middleware
You may find a PSR-15 Middleware class already written that will satisfy your needs. Here are a few unofficial lists to search.